What is BIM, and How does it impact the construction industry
-
Sapna
- April 10, 2024

Building Information Modeling, or BIM, is a game-changing process that is revolutionising the construction. BIM in construction is a 3D model-based process that enables all construction professionals to plan, design, construct, and handle buildings and infrastructure more efficiently.

The first BIM software that resembled modern BIM tools was introduced in the late 1980s and early 1990s. Autodesk Revit, one of the most well-known BIM software, was released in 2000. Since then, BIM software has evolved significantly, with numerous other companies developing their BIM tools and platforms.
In this blog, we’ll explore the role of BIM in the construction sector and its far-reaching implications for project management, cost reduction, and sustainability.
Table of Contents
ToggleWhat is BIM or Building Information Modeling?
BIM, or Building Information Modeling, is a digital tool used in construction. It generates a 3D model of a building, showing its physical and functional features. This model helps architects, engineers, and builders work together more efficiently.
It allows all stakeholders to plan, design, build, and manage buildings better. It also helps in reducing errors and saving time and money. The BIM model is like a shared knowledge resource that everyone involved in the building process can use to make informed decisions.
How can BIM help you?
Building Information Modeling (BIM) enhances construction projects by improving stakeholder collaboration, allowing for precise cost estimation, and offering detailed 3D visualisation for better design decisions. It aids in detecting potential clashes before construction, reduces rework, and provides a digital record for efficient facility management post-construction.
Benefits of BIM

Here are five benefits of Building Information Modeling in construction:
- It provides valuable data for building operations, maintenance, and renovations, supporting efficient facility management throughout the building’s lifecycle
- It tools throughout all project phases ensure higher-quality builds by enabling better control over design and construction decisions.
- BIM can assist in analysing and optimising buildings’ energy performance and sustainability, contributing to greener construction practices.
- It enables more effective project management by providing a comprehensive and integrated platform for tracking progress, managing resources, and making informed decisions.
- BIM enables model-based cost estimation, leading to more accurate budgeting and cost management throughout the project lifecycle.
What are the BIM standards?
BIM standards are consensus-based guidelines defining the methods and best practices for using Building Information Modeling in constructing and managing built assets. The National BIM Standard-United States is an example of such a standard, providing a framework for collaboration and data exchange among all parties involved in the built environment. It encompasses existing standards, documentation of information exchanges, and best business practices (National BIM Standard) (National Institute of Building Sciences).
What are BIM dimensions?
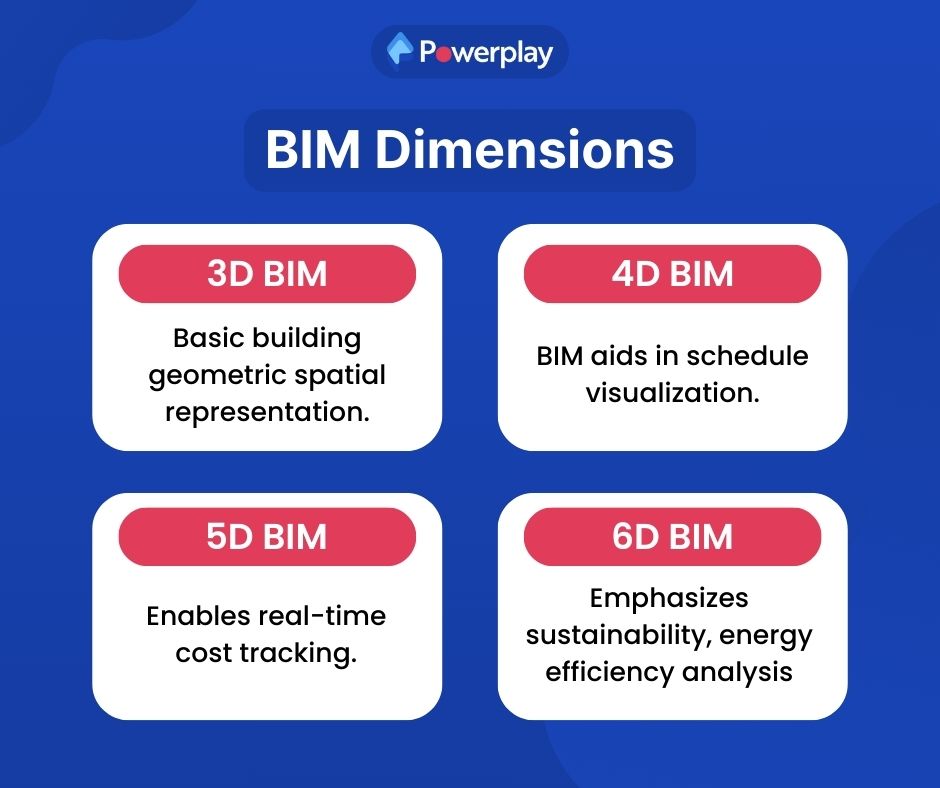
BIM dimensions refer to the different aspects of information that can be incorporated into a BIM model. These dimensions typically include:
- 3D: The basic geometric and spatial representation of the building.
- 4D: Adds the element of time, allowing for schedule and construction sequencing visualisation.
- 5D: Incorporates cost estimation and budget analysis, enabling real-time cost tracking.
- 6D: Focuses on sustainability and energy efficiency, helping in the analysis of a building’s environmental impact
What is a BIM object?
A Building Information Modeling object digitally represents a physical product or construction element within a BIM model. It contains detailed information, such as geometrical data, material properties, and functional characteristics, which can be used for various purposes, including visualisation, simulation, and analysis. BIM objects are essential components of a BIM model, enabling accurate and comprehensive representation of the building design.
From Blueprints to CAD to BIM
The transformation from blueprints to CAD to Building Information Modeling represents the evolution of architectural and engineering design. Blueprints, hand-drawn on paper, gave way to Computer-Aided Design (CAD), which allowed for digital 2D and 3D modeling.
Building Information Modeling further advanced this by incorporating detailed building information, enabling better collaboration and efficiency throughout a building’s lifecycle. This progression reflects a shift towards more integrated and information-rich construction and building managementapproaches.
BIM Objects
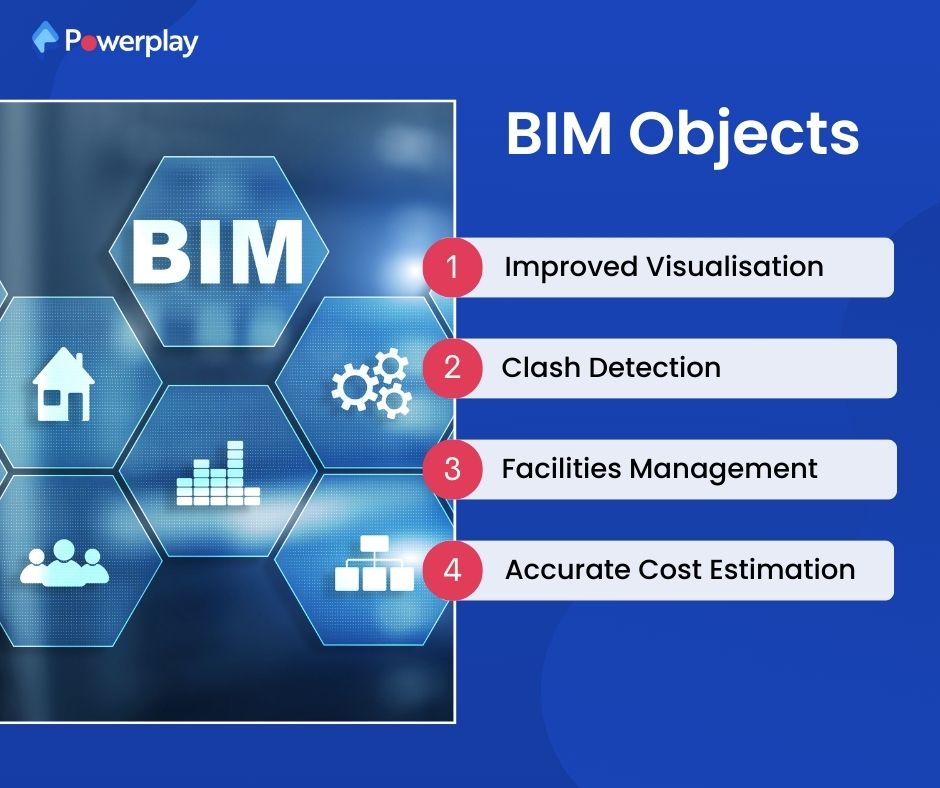
- Improved Project Visualisation: It allows for creating detailed 3D models, enabling better project visualisation and aiding in design decisions and client presentations.
- Clash Detection: It helps identify potential clashes between different building systems (e.g., structural, mechanical, electrical) before construction, reducing the need for rework.
- Facilities Management: It provides a digital record of building information that can be used for efficient maintenance and management of the facility post-construction
- Accurate Cost Estimation: It enables more precise cost estimation by providing detailed information about materials, labour, and other expenses, helping to reduce budget overruns.
The “I” in BIM
The “I” in BIM stands for “Information.” It represents the crucial data and knowledge embedded within the Building Information Modeling process. This information encompasses all aspects of a building’s physical and functional characteristics and is used to support decision-making across the building’s lifecycle, from initial planning to construction and beyond.
How Is BIM Information Shared?
BIM information is shared through a Common Data Environment (CDE), a mutually accessible online space. This environment allows stakeholders to access and manage information models throughout every stage of a building’s life. The CDE ensures that all project information, whether in BIM environments or conventional data formats, is shared using a single collaborative data environment.
Importance of Building Information Modeling
Building Information Modeling (BIM) is important because it enables improved coordination among design and construction professionals. This leads to more accurate cost estimating, reduced need for change orders, fewer surprises during construction, and a better understanding of a building’s potential performance.
BIM also improves facilities management after construction is complete, providing a digital record of building information that can be used for maintenance, space planning, and asset management.
How Does the BIM Process Work?
The BIM process involves creating a digital showcase of all a building’s characteristics through computer-aided design (CAD). This model is used for various purposes, such as construction planning, cost estimation, and facilities management. The BIM process results in a Building Information Model that contains details about every aspect of the building. This model improves accuracy, expresses design intent, transfers knowledge, reduces change orders, and provides insight into existing buildings for future projects.
What Can BIM Do?

Building Information Modeling can do various tasks, such as:
- Visualise and Analyse Building Designs: It allows for the creation of detailed 3D models that can be used to visualise and analyse building designs, facilitating better decision-making and design optimisation.
- Generate Construction Documents: It can automate the generation of construction documents, ensuring consistency and accuracy across all project documentation.
- Coordinate Work Among Professionals: It enables effective coordination among architects, engineers, and construction professionals, reducing conflicts and improving project outcomes.
- Create Virtual Walk-throughs: It models can create virtual walk-throughs of buildings, allowing stakeholders to explore the design and identify potential issues before construction.
- Estimate Costs More Accurately: By incorporating detailed information about materials, labour, and equipment, BIM can help estimate project costs more accurately, reducing the likelihood of budget overruns.
What are BIM Levels?
Building Information Modeling Levels are a way to measure the adoption and integration of Building Information Modeling within construction projects and organisations. They indicate a project’s collaboration, digitalisation, and information management degree. There are various BIM levels, such as Level 0, Level 1, Level 3, and Level 4, 5, and 6 BIM.
Here’s a detailed explanation of the types of Building Information Modeling Levels:
Level 0 BIM: Paper-based drawings + zero collaboration
At level 0, BIM is not used. Drawings and documentation are created and managed in 2D formats, typically CAD software. Information is shared through paper or electronic prints.
Level 1: 2D construction drawings + 3D modeling
Level 1 involves using both 2D and 3D CAD systems, but not in a collaborative environment. 3D models are used primarily for visualisation but are not linked to any data. At this level, Information is managed and shared electronically.
Level 2: Teams work on their 3D models
In the level 2 stage, different stakeholders create separate 3D models, but there is more collaboration between parties. A Common Data Environment (CDE) is used to share information and exchange Building Information Modeling data between parties in a standardised format, such as IFC (Industry Foundation Classes).
Level 3: Teams work with a shared 3D model
Level 3 represents the full integration of BIM throughout the project lifecycle. All parties work on a single, shared model stored in a central repository. Information is updated in real time, and changes are reflected across all model views. This level also includes the use of advanced technologies like 4D (time), 5D (cost), and 6D (sustainability) BIM.
Levels 4, 5, and 6: Adding in scheduling, cost, & sustainability information
At level 4, the Building Information Modeling process is optimised for greater efficiency and effectiveness. This involves using predictive analytics, machine learning, and other advanced technologies to optimise project outcomes.
Tips for Getting Started With BIM in Your Business
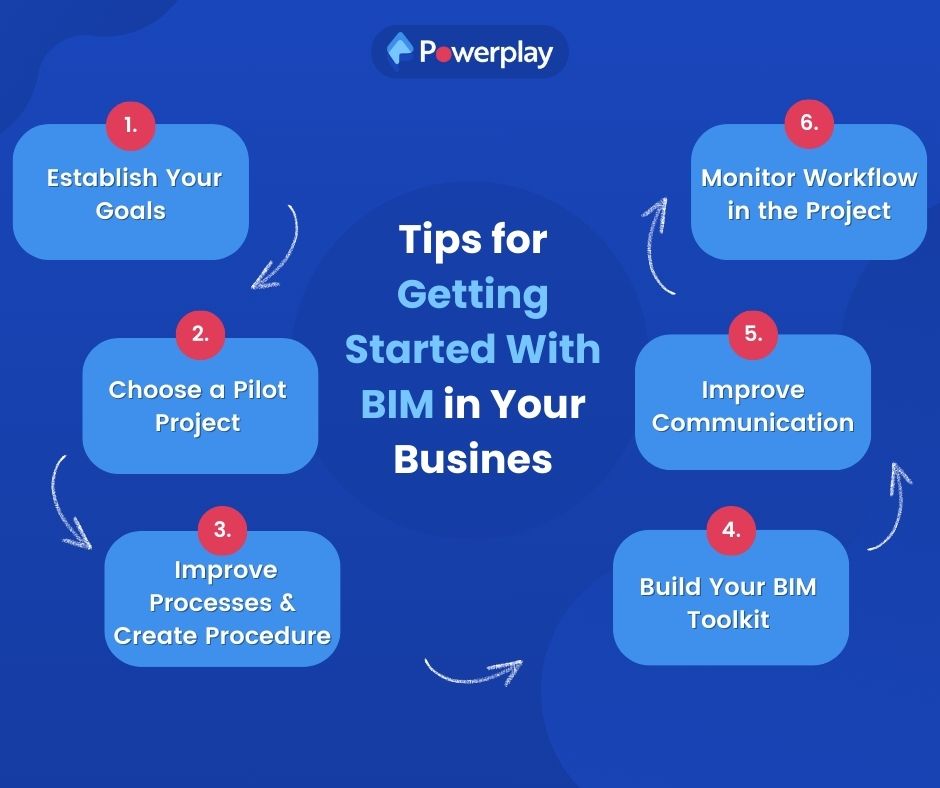
Here are some tips for getting started with Building Information Modeling in the construction business:
Step 1 – Establish Your Goals:
Before diving into Building Information Modeling, determine what you want to achieve. Do you want to improve collaboration, reduce errors, or enhance project efficiency? Setting clear goals will help guide your Building Information Modeling implementation strategy.
Step 2 – Choose a Pilot Project:
Start small by selecting a pilot project to test BIM. Choose a project that’s manageable in size and complexity. It will allow you to learn and adjust your approach before rolling out BIM on larger projects.
Step 3 – Improve Processes and Create Procedures:
BIM is not just about technology; it’s also about processes. Review and improve your existing workflows to ensure they align with Building Information Modeling practices. Develop standard procedures for using BIM in your projects.
Step 4 – Build Your Building Information Modeling Toolkit:
Create a ‘BIM toolkit’ that includes the necessary software, hardware, and training resources. Assure your team is equipped with the tools and knowledge to use Building Information Modeling effectively.
Step 5 – Improve Communication:
It enhances collaboration among project stakeholders. Foster open communication channels and encourage team members to share information and insights. This will help you leverage BIM’s full potential.
Step 6 – Monitor Workflow in the Project:
Track the progress of your BIM model implementation in the pilot project. Monitor how workflow impacts and find out sectors for improvement. Use all these insights to refine your approach for other projects.
Impact of BIM on the Construction Industry

Building Information Modeling, has had a significant impact on the construction industry in various ways, such as:
Enhanced Collaboration and Communication
The Building Information Modeling process fosters stakeholder collaboration by giving a shared platform for accessing and updating project information. This leads to better coordination, fewer errors, and a more streamlined workflow.
Cost Reduction and Budget Management
By identifying potential design clashes and conflicts early in the design phase, Building Information Modeling reduces the need for costly rework and delays, helping manage budgets more effectively.
Improved Productivity
It streamlines workflows and processes, increasing productivity and efficiency on construction sites. This is achieved through better resource allocation, optimised scheduling, and eliminating unnecessary tasks.
Data-Driven Decision Making
The Building Information Modeling process provides a wealth of data and information to inform decision-making throughout the project lifecycle. This includes everything from material specifications to energy performance analysis.
Enhanced Safety and Risk Management
By visualising and analysing potential safety hazards in the digital model, BIM helps improve safety on construction sites and reduces the chances of accidents.
Sustainability and Environmental Considerations
The Building Information Modeling model facilitates the design and construction of more sustainable buildings by enabling the analysis of energy consumption, material efficiency, and environmental impact.
What is the future of BIM?
The future of Building Information Modeling in construction will be more integrated and automated. It is likely to become more closely interlinked with software like artificial intelligence, virtual reality, and the Internet of Things.
These advancements will enable more efficient design processes, improved collaboration, and better decision-making in construction. Building Information Modeling will promote sustainability by facilitating energy-efficient designs and reducing waste. With the industry’s growing focus on digitalisation, Building Information Modelling is set to expand, making it an essential tool for future construction projects.
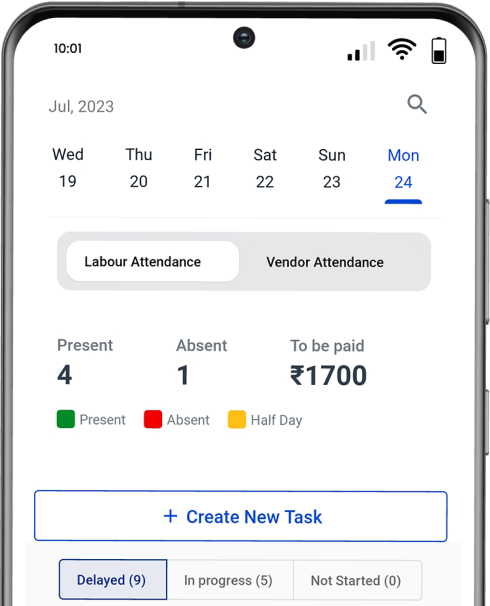
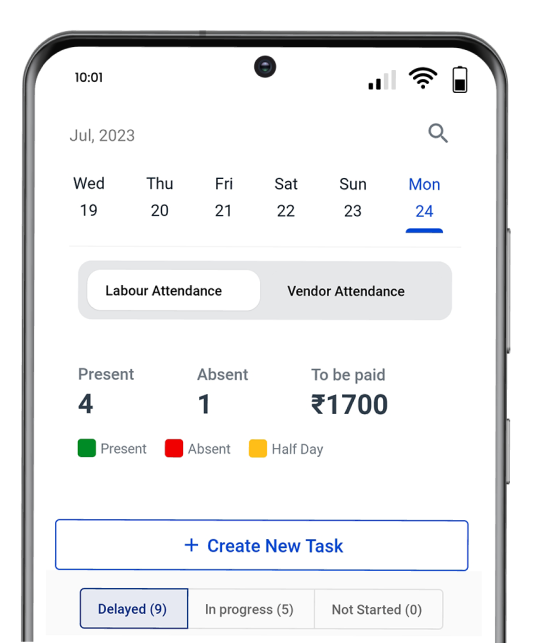
How can Powerplay Construction Project Management Software Help in BIM?
Powerplay is construction management software that can be an alternative to Building Information Modeling software for certain aspects of construction project management. It offers a wide range of user-friendly features that can streamline construction operations, making it a valuable tool for project managers, site engineers, and owners.
Powerplay allows users to manage projects on mobile, get real-time updates, enhance collaboration, and increase efficiency. It also provides real-time visibility of on-site material stock and helps fasten the procurement process to reduce material loss. With Powerplay, users can track daily expenses and categorise every expense for complete transactional reports.
Powerplay improves productivity, boosts efficiency, enhances communication, improves material and labour management, and reduces cost overruns. So download the Powerplay app now and streamline your project more seamlessly and effectively.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Building Information Modeling is overtaking traditional methods and transforming the construction industry by enhancing collaboration, reducing costs, and improving the quality of built environments. Recent studies estimate the adoption rate of the BIM model in India to be between 10-18%, and globally, expecting to grow at a CAGR of 16.33% to reach USD 23950 million by 2027.
As Building Information Modeling continues to evolve, its impact is increasing, making it an essential tool for the industry’s future. So, embrace BIM to drive sustainability, innovation, and precision in your construction projects.