Different Building Materials For Construction Every Builder Should Know
-
Sapna
- April 19, 2024

In this modern era, the choice of materials is not only about aesthetics and durability of a structure but also its functionality and environmental impact. As the construction industry evolves from the foundational strength of concrete and steel to the aesthetic versatility of wood and glass, understanding the various building materials used in house construction is essential for builders to achieve rapid growth in their projects.

In this blog, we will explore list of construction building materials, discussing their roles, benefits, and considerations. Learn about all the factors involved in choosing the right materials to ensure the success of your projects.
Table of Contents
ToggleThe Importance of Building Materials Management
Choosing the right materials used in construction is fundamental to the success of any construction project, as they impact many main aspects like structural integrity, energy efficiency, and aesthetic appeal. So, selecting high-quality materials to ensure durability and safety to maintain costs and extend the lifespan of a structure is critical.
The right materials can also enhance a building’s energy efficiency, leading to significant savings and reduced environmental impact. In the case of designs, materials influence spaces’ visual and tactile qualities, affecting how people experience and interact with their environments.
Therefore, the thoughtful selection of building materials is crucial in achieving desired outcomes in construction, functionality, and sustainability.
Understanding Material Properties
Understanding all the properties of materials is vital when selecting the right components for any construction project. Following mentioned properties have significant impact on the performance and longevity of the finished structure, so before choosing the material ensure they contain all the below mentioned properties. The understanding of material properties is also crucial in the management and optimization of material in construction projects, encompassing strategies like just-in-time inventory, reduction of material waste, and enhancement of material transport efficiency.
Strength:
This is essential for the structural integrity of a building. Materials must withstand loads and stresses over time without failure, ensuring the safety and stability of the structure.
Durability:
Durable materials resist weathering, wear, and degradation, thereby extending the life of the building and reducing the requirement for frequent repairs and replacements, which can be costly and disruptive.
Sustainability:
Choosing sustainable materials is increasingly important in reducing the environmental impact of construction. Sustainable materials are sourced responsibly, have a lower carbon footprint, or are made from recycled components. These choices help promote environmental stewardship and lead to better building performance and lower operating costs.
Cost:
Budget constraints often dictate material choices. It’s important to consider the initial cost and the long-term cost implications of materials, including maintenance, repair, and replacement costs. Investing in higher-quality materials upfront can be cost-effective over the building’s lifecycle.
Essential Types of Building Materials Every Builder Should Know
Construction materials can generally be classified into three main categories: structural, non-structural, and speciality. Each of these categories plays a crucial role in the building process, serving different functions and purposes. Understanding the supply chain is essential for ensuring the availability and timely delivery of these materials, which is critical for the success of any construction project.
So, let’s learn about these categories in detail:
Structural Materials
Structural materials form the backbone of every construction project, providing the necessary support and stability to buildings and other structures. These materials include concrete, steel, wood, and masonry, each possessing unique properties and applications suited to different aspects of construction.
Concrete

Concrete is a fundamental construction material known for its strength and versatility. It is widely used in various construction applications, including building foundations. Due to its strength, concrete provides a solid and stable base that is necessary to support the weight of the entire structure. It is also used in constructing slabs, such as floors and driveways. Slabs are favoured for their durability and ability to withstand heavy loads and traffic, which is essential in areas subject to frequent use.
It is categorised into two primary types that are:
- Ready-mix: This concrete is prepared at a batch plant according to a set recipe and then transported to a site in a rotating drum mixer. It’s used for convenience and quality control and is ideal for large-scale construction projects where consistency and timely delivery are critical.
- Precast Concrete: It is manufactured in a controlled environment and transported as ready-to-install components. It is used for specific, repetitive elements like floor slabs, staircases, or wall panels. This method ensures faster construction times and better quality control.
Steel

Steel is a major structural material valued for its strength, flexibility, and fire resistance. It is adaptable to various architectural designs and structural requirements. It offers advantages, like high tensile strength and the ability to withstand seismic forces, which make it indispensable in high-rise buildings, bridges, and industrial structures.
There are different sections of steel, such as:
- Beams: Typically used to support floors or roofs.
- Columns: Employed to carry compressive loads, making up the vertical supports of structures.
Wood

Wood is considered natural and renewable, as it offers a combination of aesthetic appeal and structural capability. It is used for framing, roofing, and adding aesthetic value to interiors and exteriors through finishes and furnishings.
There are various types of wood used in construction, such as:
- Lumber: Solid wood is commonly used for framing due to its strength and flexibility.
- Engineered Wood: These include products such as plywood, oriented strand board (OSB), and glue-laminated timber (glulam), offering extra durability and resistance to environmental factors.
Masonry

Masonry construction involves assembling units of materials such as bricks and blocks with mortar. It is valued for its durability, fire resistance, and thermal mass, making it ideal for walls, chimneys, and decorative elements. All these materials contribute to the diverse possibilities in construction, catering to different structural needs and aesthetic preferences.
Masonry types include:
- Bricks: Typically made of clay, they are used for their durability and aesthetic appearance.
- Concrete Blocks: Larger than bricks and are used in foundations and load-bearing walls.
Non-Structural Materials
Non-structural materials are vital for a building’s finishing, insulation, and aesthetics, often contributing significantly to its energy efficiency and comfort. These materials include a wide range of products suited for roofing, insulation, interior finishes, and installing doors and windows.
There are various types of Non-Structural Materials, which include:
Roofing Materials

Roofing materials are critical for protecting a building from the elements and can affect its aesthetic appeal and energy efficiency. There are various standard roofing options, which include:
- Asphalt Shingles: They are the most popular roofing material in many regions. They are valued for their cost-effectiveness and straightforward installation. They are suitable for various residential projects and come in various colours and styles.
- Metal Roofing: Metal Roofing is mainly known for its durability and resistance to extreme weather. It is the best choice for residential and commercial buildings. It reflects solar radiant heat, which can help reduce cooling costs and is recyclable, enhancing its environmental appeal.
- Green Roofs: Green roofs are part of an eco-friendly approach to roofing, where the roof is partially or completely covered with vegetation placed over a waterproofing membrane. They are excellent for urban environments and provide insulation, reduce stormwater runoff, and also help to combat the heat island effect.
Insulation Materials
Proper insulation is crucial for maintaining a building’s thermal efficiency, comfort, and energy consumption. There are various types of insulation, such as:
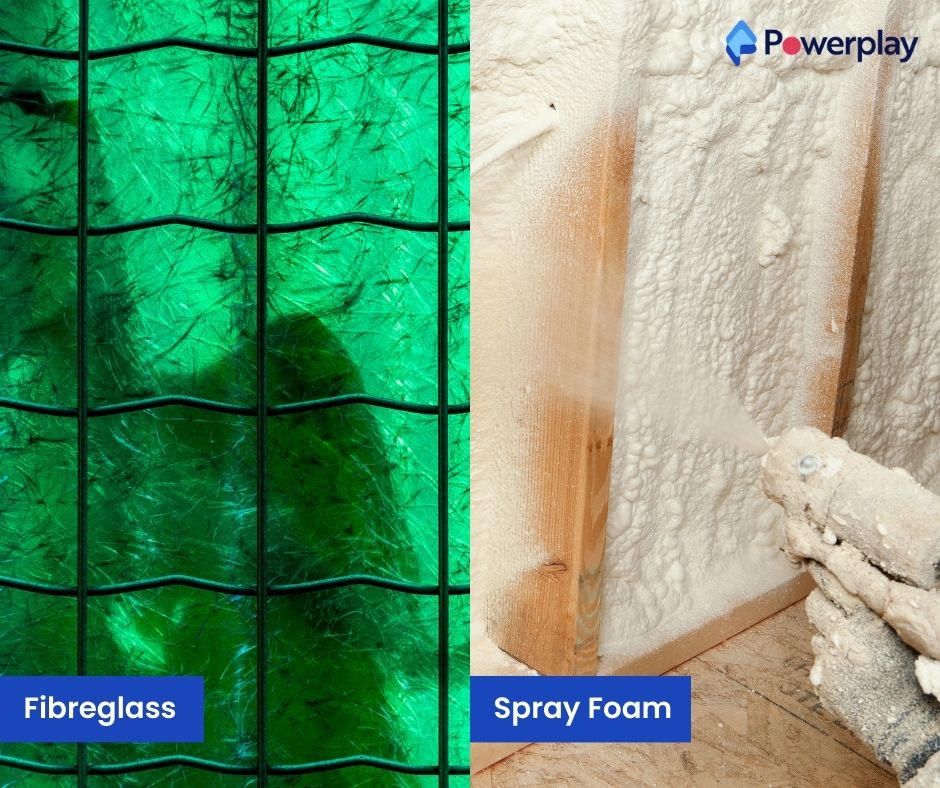

- Fibreglass: Comprising fine glass fibres, fibreglass is commonly used in batts, rolls, and loose-fill insulation. It is non-flammable and effective at minimising heat transfer, making it ideal for residential and commercial walls, attics, and floors.
- Spray Foam: This insulation forms an airtight seal and is excellent for filling gaps and reducing air leakage. It comes in open-cell and closed-cell forms, the latter providing higher R-value per inch for greater thermal resistance and strength.
Interior Finishes
Interior finishes enhance the aesthetic appeal and functionality of indoor spaces. You can see various interior materials such as:

- Walls: Drywall is widely used due to its quick installation and smooth finish, which makes it suitable for painting or wallpapering. Plaster, though more labour-intensive, provides a durable and high-quality finish.
- Ceilings: Options include plaster for a seamless finish and suspended ceilings, which allow easy access to ducts and wiring while providing sound dampening.
- Flooring: Choices range from ceramic tiles and hardwood, which add elegance and durability, to carpet, which offers warmth and comfort underfoot
Doors and Windows
The materials used for doors and windows impact a building’s energy efficiency, security, and aesthetics, and there are different types of door and window materials available, such as:
- Wood: Offers natural beauty and insulation properties but requires maintenance to prevent weathering.
- Steel: Highly secure and durable, ideal for exterior doors.
- Vinyl: Common for windows, it offers excellent thermal insulation and is resistant to moisture and decay.
Speciality Materials
Specialty materials in construction include a variety of innovative and function-specific products designed to enhance the performance, sustainability, and aesthetics of buildings. These include advanced glass and glazing options, geotechnical materials for soil and foundation stability, and sustainable materials that support environmental conservation.
Glass and Glazing

Architectural glass is a critical material in modern construction. It is known for its transparency and ability to admit natural light while providing insulation and energy efficiency. Designers use it in a variety of ways, such as in windows, where it offers beautiful views and light access, and in curtain walls, where it creates striking glass facades.
Different types of glazing techniques are:
- Double Glazing: Includes two layers of glass with an air or gas-filled space between them, significantly improving thermal and acoustic insulation.
- Low-Emissive (Low-E) Glazing: This glass has a microscopically thin coating that reflects heat, keeping spaces warm in winter and cold in summer and reducing UV light transmission.
Geotechnical Materials
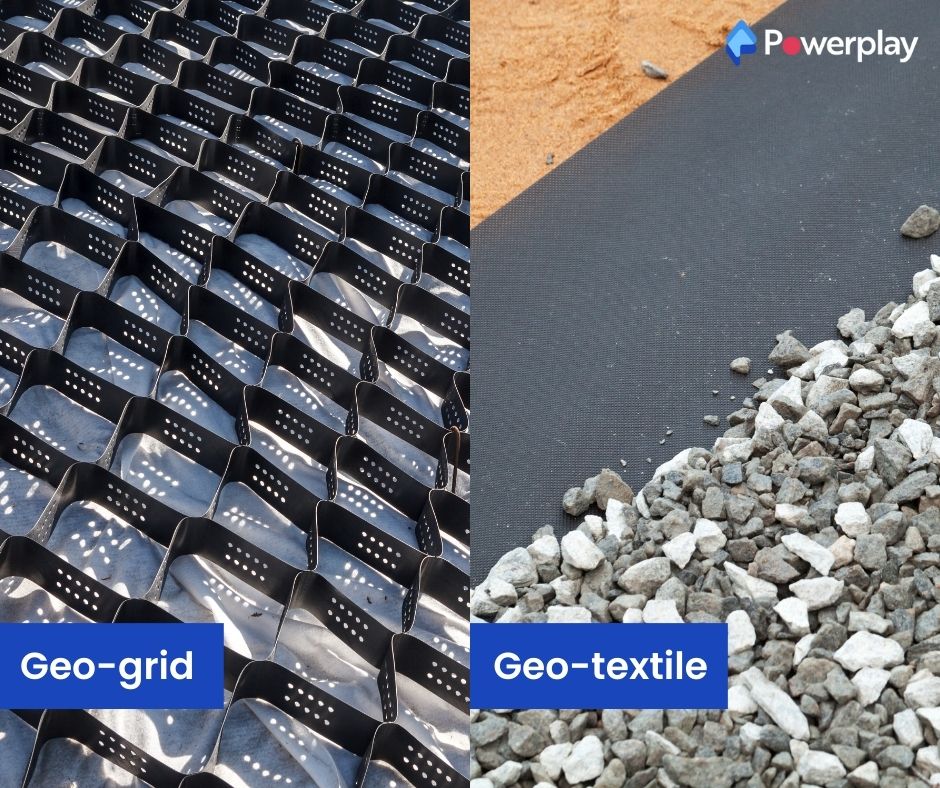

Geotechnical materials are used to solve problems related to soil mechanics and foundation engineering, improving the stability and durability of construction projects.
- Geotextiles are permeable fabrics that, when used in soil, can filter, separate, reinforce, and protect, making them ideal for roadworks and erosion control.
- Geogrids offer a structured grid system that reinforces soil, enhancing load distribution in roadbeds and behind retaining walls.
These materials are crucial for projects requiring soil stabilisation, effective drainage, and foundational support, ensuring the long-term integrity and safety of the structures.
Sustainable Materials

The importance of sustainable building materials has escalated as the industry aims to reduce its environmental impact. Adopting these materials not only supports environmental sustainability but also offers builders and homeowners long-term savings through energy efficiency and reduced maintenance. It includes different types of materials, such as:
- Recycled Content Concrete: Incorporates recycled materials like crushed glass or slag from industrial processes, reducing waste and often improving the concrete’s thermal and acoustic properties.
- Bamboo: Fast-growing and with a high strength-to-weight ratio, bamboo is an excellent renewable resource for flooring, panelling, and structural elements in eco-friendly construction.
- Low-VOC Paints: These paints minimise the release of volatile organic compounds, improving indoor air quality and reducing pollution.
Choosing the Right Building Materials
Selecting the right building materials is important for the success of any construction project. Management is crucial in this process, as builders must consider a variety of factors to ensure that they choose materials that meet their project’s requirements effectively while following all the regulations and sustainability goals. Materials management plays a pivotal role in ensuring the right materials you need choose to meet these needs.
Here are a few factors which you need to consider before choosing any materials for your projects:

- How materials management is integral to aligning with project requirements is a critical consideration. Builders must assess the durability, cost, and aesthetic appeal of materials in relation to the project’s needs.
- The relevance of materials management in adhering to building codes and regulations cannot be overstated. It ensures that materials not only meet the structural requirements but also comply with local and international standards for safety and sustainability.
- One of the critical considerations in material selection is how well materials can adapt to the local climate, affecting both the longevity and efficiency of the construction project.
1. Project Requirements
The nature of the project dictates the materials needed in terms of structural integrity, functionality, and aesthetics. For instance, structural loads require materials with sufficient strength and durability, such as reinforced concrete for foundations or steel for frameworks. Functionality might influence choices like soundproof walls for a theatre or water-resistant materials for bathrooms. Aesthetics also play a significant role, as the appearance of materials should align with the desired architectural style and finish.
2. Building Codes and Regulations
Every region has specific building rules and regulations that ensure safety, health, and environmental protection. These regulations mandate the use of certain materials in specific applications and set standards for construction practices. Compliance is not just a legal need but also a guarantee of safety and quality in building construction.
3. Climate and Environment
The local climate significantly influences material selection. For example, areas prone to hurricanes may require impact-resistant materials for windows and doors, while cold climates necessitate high-insulation materials to conserve heat. Additionally, environmental factors such as soil type can affect choices in foundational materials to prevent issues like subsidence.
4. Budget and Cost Considerations
Budget constraints are a critical factor in material selection. It’s important to balance cost with quality to ensure that the building is both economically viable and durable. Choose cost-effective materials without compromising the essential qualities needed for the specific functions of the building.
5. Sustainability Goals
With increasing awareness of environmental impacts, choosing sustainable materials has become vital. Options like recycled materials, sustainably sourced wood, or low-VOC paints help reduce the environmental footprint of a project. These materials not only help in achieving green building certifications but also contribute to long-term cost savings through energy efficiency and durability.
Conclusion
Understanding different building materials is paramount in the construction industry, as the selection of these materials directly influences the success of any project. Selecting the right materials affects everything from structural integrity to sustainability, impacting both the durability and functionality of the finished structure.

Material selection not only ensures the project meets specific performance requirements but also influences overall project costs and environmental impact. As the construction industry evolves, new and innovative materials continue to emerge, offering enhanced properties and efficiencies. Builders must stay informed about these developments to adopt advanced solutions that could provide competitive advantages and lead to more successful projects.
Embracing innovation in material technology is an important factor in building safer, more sustainable, and cost-effective structures. So, if you have not yet adopted the construction material management software, then download the Powerplay app now. As it is India’s best construction management software that helps to manage the materials and many other aspects of construction more effectively and efficiently.