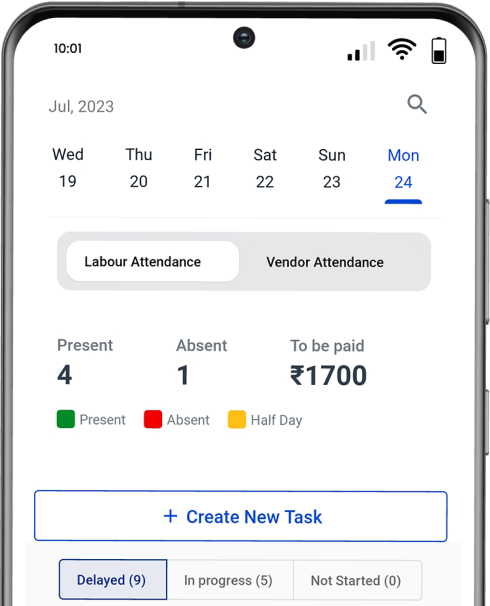
Quality Control in Construction Projects: A Comprehensive Guide
-
Kumar Abhishek Anand
- February 14, 2024

Quality control (QC) in construction projects is the process of ensuring that construction projects meet all applicable standards and requirements. It is an essential part of any construction project, as it helps to reduce the risk of defects and problems, which can save time and money in the long run.
There are a number of different quality control activities that can be carried out on a construction project. These activities can be divided into two main categories: preventive and corrective.
- Preventive quality control activities are aimed at preventing defects from occurring in the first place. This includes activities such as developing quality control plans, inspecting materials and equipment, and training workers on quality control procedures.
- Corrective quality control activities are aimed at identifying and correcting defects that have already occurred. This includes activities such as inspections, testing, and documentation reviews.
Table of Contents
ToggleWhy is quality control important in construction projects?
Quality control is important in projects for a number of reasons. First, it helps to ensure that projects are completed to the required standards and that they meet the needs of the client. Second, quality control helps to reduce the risk of defects and problems, which can save time and money in the long run. Third, quality control helps to improve the reputation of the construction company and its employees.
Benefits of effective quality control

Effective quality control can lead to a number of benefits, including:
- Reduced costs: Effective quality control can help to reduce costs by preventing defects and problems from occurring in the first place.
- Improved efficiency: Effective quality control can help to improve efficiency by streamlining processes and reducing the need for rework.
- Increased customer satisfaction: Effective quality control can help to increase customer satisfaction by delivering projects that meet or exceed expectations.
- Improved reputation: Effective quality control can help to improve the reputation of the construction company and its employees.
The 5 steps of quality control in construction projects

The five steps of quality control in construction are:
- Planning: The first step of quality control is to develop a quality control plan. This plan should identify the specific quality standards and requirements for the building project, as well as the procedures that will be used to monitor and measure building quality.
- Execution: The second step of quality control is to implement the quality control plan. This includes conducting inspections, identifying defects, and taking corrective action.
- Inspection: The third step of quality control is to inspect the structures that has been built to ensure that it meets the required quality standards. Inspections can be conducted by the project manager, the quality control team, or a third party.
- Corrective action: If any defects are identified during the inspection process, corrective action must be taken to correct the defects. This may involve redoing the work, replacing materials, or making changes to the design.
- Prevention: The fifth and final step of quality control is to take steps to prevent defects from occurring in the first place. This may involve improving training, developing new procedures, or investing in new equipment.
5 basic elements of quality control in construction

The basic elements of quality control in construction are:
- Materials: The quality of the materials used in a construction project is essential to ensuring the overall quality of the project. It is important to use materials that meet all applicable standards and specifications.
- Workmanship: The workmanship of the workers on a construction project is also essential to ensuring the overall quality of the project. It is important to hire qualified and experienced workers, and to provide them with the training and resources they need to do their jobs well.
- Equipment: The equipment used on a construction project can also have an impact on quality. It is important to use well-maintained and calibrated equipment.
- Procedures: The procedures that are followed during construction can also have an impact on quality. It is important to have well-defined and documented procedures in place, and to ensure that all workers follow these procedures.
- Documentation: Documentation is an important part of quality control. It is important to document all inspections, tests, and corrective actions that are taken. This documentation can be used to track progress, identify areas for improvement, and provide evidence of quality to clients.
Who is responsible for quality control?
The project manager is ultimately responsible for quality control on a construction project. However, all members of the project team have a role to play in ensuring quality. This includes the quality control team, the workers, and the suppliers.
Construction management software
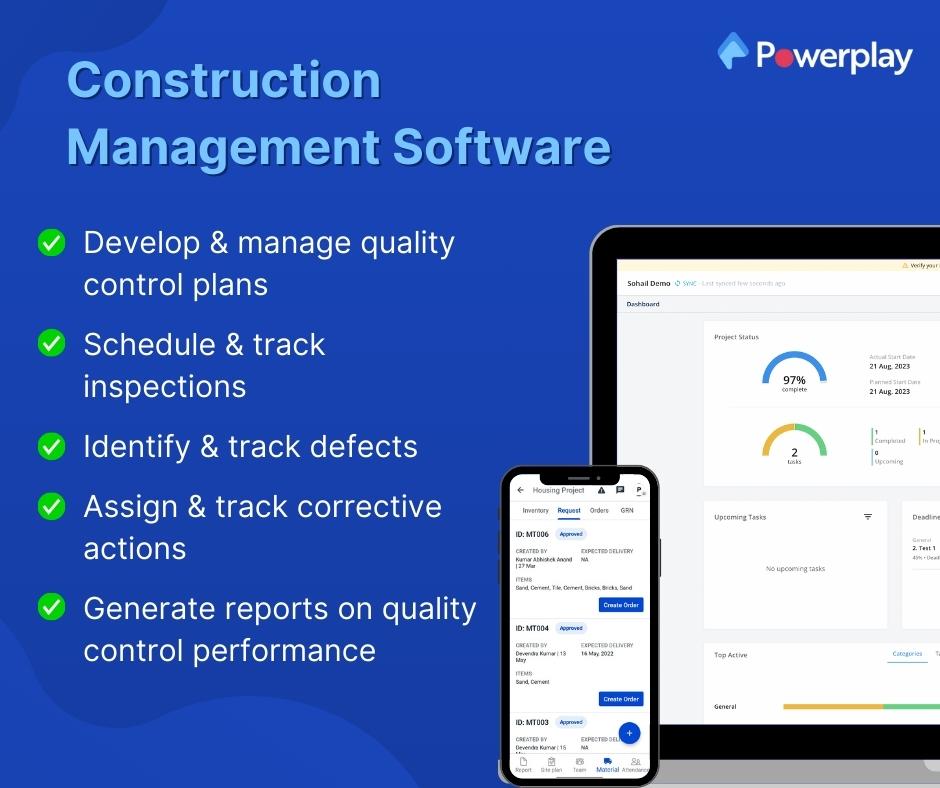
Construction management software can help construction teams to improve their quality control processes in a number of ways. For example, construction management software can be used to:
- Develop and manage quality control plans
- Schedule and track inspections
- Identify and track defects
- Assign and track corrective actions
- Generate reports on quality control performance
Construction management software can also help to improve communication and collaboration between members of the project team. This can be especially beneficial for quality control, as it allows everyone involved to stay informed of the latest developments and to work together to resolve problems quickly and efficiently.
Powerplay

Powerplay is a construction management software system that can help construction teams to improve their quality control processes. Powerplay provides a variety of features that can be used to manage quality control tasks, such as:
- Customizable checklists for inspections
- Task management tools for assigning and tracking corrective actions
- Reporting tools for tracking and analyzing quality control performance
It is also a mobile-friendly platform, so construction teams can access their quality control information from anywhere. This makes it easy for construction teams to stay on top of their quality control processes, even when they are working on multiple projects at different locations.
Conclusion
Quality control is an essential part of any construction project. By following the five steps of quality control, construction teams can reduce the risk of defects and problems, and improve the overall quality of their projects. Construction management software, such as Powerplay, can help construction teams to improve their quality control processes by providing them with the tools they need to plan, schedule, track, and report on their quality control activities.
Share
Kumar is a digital content professional with more than 2 years of experience in Blog writing, copywriting and scripting. His passion lies in the art of creating convincing content that plays a major role in converting leads for SAAS businesses.